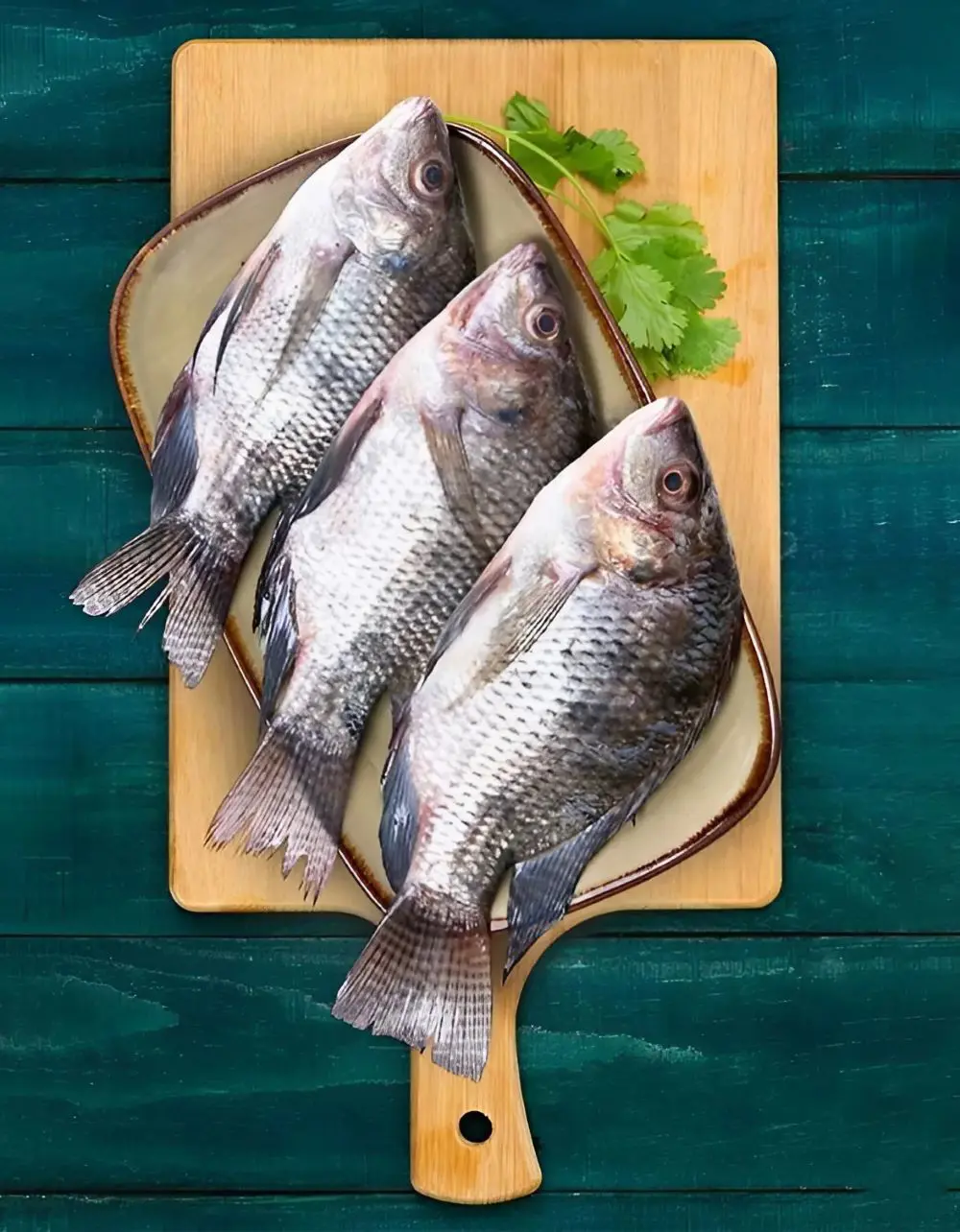
Tilapia is a freshwater fish species known for its mild flavor and versatility in cooking. It has risen to prominence as one of America's most popular fish choices due to its affordability, mild taste, and ease of preparation.
In its natural state, tilapia is low in calories and sodium, making it a healthy choice packed with essential vitamins and minerals. Here is the tilapia nutrition breakdown and the 20 health benefits associated with its consumption.
Tilapia Nutritional Value

Known for its abundance of lean protein and wealth of vitamins and minerals, tilapia stands as a nutritious seafood choice. Let's explore tilapia nutritional content, based on a 100-gram serving, as outlined by the USDA.
- Calorie: 128
- Carbs: 0 grams
- Fats: 2.65 grams
- Protein: 26.2 grams
- Calcium: 14 mg
- Iron: 0.69 mg
- Magnesium: 34 mg
- Phosphorus: 204 mg
- Potassium: 380 mg
- Sodium: 56 mg
- Selenium: 54.4 µg
- Thiamin: 0.093 mg
- Riboflavin: 0.073
- Niacin: 4.74 mg
- Vitamin B-6: 0.123
- Folate: 6 µg
- Choline: 51.3 mg
- Vitamin B-12: 1.86 µg
Health Benefits of Tilapia
Similar to other seafood options, incorporating tilapia into your diet offers numerous health benefits, including enhanced heart health, weight management support, potential anticancer properties, and beyond. In this discussion, we will delve into 20 detailed benefits of consuming tilapia.
1. Healthy Source of Protein

A 100-gram portion of cooked tilapia offers 26.2 grams of protein, making it an excellent source of lean protein. Protein is a crucial dietary component, especially animal-derived proteins, as they are broken down into amino acids and restructured into functional proteins within the body.
This process is vital for the growth and maintenance of organs, tissues, cells, and muscles. Protein is also crucial for producing hormones and enzymes that support proper bodily functions.
2. May Improve Heart Health

A significant reason why eating fish is healthy is because it's rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These fats contribute to heart health by reducing blood clotting, lowering blood pressure, and decreasing the risk of stroke, heart failure, and irregular heartbeats.
While tilapia has fewer omega-3 fatty acids than oily fish like salmon, it contains more than other protein sources such as beef or chicken. It's also high in omega-6 fats, which are essential but often overconsumed compared to omega-3s, leading to an imbalance that isn't ideal for overall health.
3. May Have Anticancer Properties
Selenium, a trace mineral, is well-known for its potential to reduce free radical activity in the body, potentially lowering the risk of oxidative stress on all organ systems and the transformation of healthy cells into cancerous ones.
While the body needs selenium in small amounts, it plays a crucial role in various bodily processes. Tilapia is an excellent source of this mineral, with just one fillet providing 88% of your daily recommended intake of selenium.
4. Promotes Weight Loss
Tilapia can contribute to weight management for several reasons. Firstly, it has a lower calorie content compared to other protein sources, which helps create a calorie deficit for weight loss. Secondly, it serves as a lean protein source, promoting feelings of fullness and reducing the temptation to overeat.
Moreover, tilapia is low in carbohydrates and saturated fat, making it an ideal option for those seeking to manage their calorie intake while still obtaining vital nutrients for overall health and weight control.
5. May Improve Brain Health
Including tilapia in your diet can enhance brain function due to its omega-3 content, which promotes neurological function and offers neuroprotective effects. Additionally, tilapia is rich in selenium, which has been shown to protect the brain against conditions such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and epilepsy.
Selenium enhances oxygen flow to the brain, aiding in fluid balance throughout the body and promoting mental clarity. Thus, consuming tilapia not only delivers essential nutrients but also supports cognitive health.
6. Good for Bone Health

Tilapia fish can benefit bone health because it's packed with nutrients like vitamin D and essential minerals such as magnesium, calcium, and phosphorus, all crucial for bone growth and maintenance. Recent research has indicated the potential of tilapia fish collagen type 1 in regenerative medicine.
Preliminary research suggests its effectiveness in aiding bone cell regeneration in laboratory settings, and it shows promise as a scaffolding biomaterial in dentistry. However, further studies are needed to explore its full potential in these areas.
7. May Help Prevent Premature Aging
Selenium acts as an antioxidant and can revitalize and stimulate vitamins E and C, both of which contribute to skin quality and health. The abundance of selenium found in tilapia makes it an excellent dietary option for enhancing skin health and appearance by preventing free radical damage.
This can result in a decrease in wrinkles, age spots, sagging, and other signs of aging.
8. Good for Thyroid Patients
Selenium, present in tilapia, plays a crucial role in regulating the thyroid gland. It is essential for antioxidant functions and the metabolism of thyroid hormones, thus improving hormonal balance.
A properly functioning thyroid gland ensures a boosted metabolism and helps prevent weight fluctuations and other thyroid-related disorders.
9. Provides More Than 25% of Your Daily Phosphorus Needs
One serving of tilapia provides over 25% of your daily recommended intake of phosphorus, a vital mineral primarily found in bones and teeth that works with calcium to maintain their health. Phosphorus is crucial for keeping bones strong, generating energy, and facilitating muscle movement.
Additionally, it aids in filtering waste in the kidneys, managing energy storage and usage, and reducing muscle pain after exercise.
10. Provides Abundance of Vitamin D
What sets tilapia apart from other seafood is its vitamin D content, which is relatively rare in foods. Consuming vitamin D-rich foods like tilapia can help meet your nutritional needs, supporting your immune system, nerves, and muscles.
Vitamin D also aids in calcium absorption, essential for building and maintaining healthy bones and teeth. Moreover, research suggests that vitamin D may play a significant role in regulating mood and reducing the risk of depression.
11. Aids Muscle Maintenance

Tilapia can support muscle maintenance in various ways. Firstly, it is an excellent source of high-quality protein, which is vital for muscle growth and repair, providing the building blocks needed for muscle tissue.
Additionally, tilapia is low in calories and fat, making it an ideal lean protein choice for those aiming to maintain or build muscle while managing their calorie intake. The amino acids in tilapia protein are essential for muscle protein synthesis, promoting the maintenance and development of healthy muscle tissue.
12. Might Aid in Wound Healing

Tilapia can help in wound healing due to its high protein content, which is essential for the repair and regeneration of tissues. Proteins supply the necessary building blocks for new tissue formation, which is critical in the wound healing process.
Additionally, tilapia skin has been used as a biological dressing for burns and other wounds. It acts as a barrier to protect against infection, maintains moisture, and creates an optimal environment for healing.
13. Prevents Tooth Decay

Tilapia may help prevent teeth degradation due to its high protein content, which is essential for developing and maintaining healthy teeth and gums. Protein supports the formation of tooth enamel, the protective outer layer of teeth.
The fish also contains minerals like calcium and phosphorus, crucial for maintaining strong and healthy teeth. These minerals aid in tooth mineralization and can help prevent tooth decay and degradation when included in a balanced diet.
14. Helps Regulate Blood Sugar
Tilapia serves as a lean protein source, which can slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, resulting in a more gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream and potentially preventing spikes in blood sugar levels.
Being low in carbohydrates, tilapia can also be beneficial for those managing their blood sugar. However, it's crucial to consider factors such as overall diet, portion sizes, and cooking methods when including tilapia in a blood sugar management plan. Consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable for personalized guidance.
15. Low in Fat
Tilapia is generally considered low in fat, especially saturated fat, making it a popular choice for individuals seeking to reduce their fat intake or maintain a healthy weight. Its low-fat content can contribute to heart health by helping to lower levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol.
While tilapia is low in fat, it still provides essential nutrients such as protein, vitamins, and minerals. This makes it a nutritious choice for maintaining overall health and meeting dietary needs.
16. Boosts Energy Levels
Tilapia can contribute to energy levels due to its high protein content and nutrient density. Protein is essential for providing sustained energy as it helps repair and build tissues, including muscles. It also contains important vitamins and minerals, such as B vitamins, iron, and phosphorus, which play key roles in energy metabolism.
While tilapia itself doesn't directly boost energy like caffeine or sugar might, including it in a balanced diet can support overall energy levels and help maintain vitality.
17. May Improve Immune System
Selenium present in tilapia plays a significant role in supporting the immune system. It can enhance the activity of white blood cells, which protect the body against toxins and foreign invaders. Acting as an antioxidant, selenium helps to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which can contribute to immune dysfunction.
Furthermore, selenium regulates immune cell activity and promotes the production of antibodies, crucial for fighting off infections and diseases. However, it's important not to consume selenium in excess, as too much can have negative effects on health.
18. High in Vitamin B12
Tilapia contains vitamin B12 in varying amounts depending on factors such as the fish's diet and habitat. Vitamin B12 is essential for various bodily functions, including nerve function, DNA synthesis, and red blood cell formation.
Consuming tilapia as part of a balanced diet can contribute to meeting your vitamin B12 needs. Adequate intake of vitamin B12 supports overall health, helps prevent anemia, supports brain function, and maintains a healthy nervous system.
19. Low Mercury Fish

Tilapia is generally considered a low-mercury fish, making it a safer option for consumption compared to certain other fish species that may contain higher levels of mercury.
This characteristic of tilapia is particularly beneficial for pregnant women, nursing mothers, and young children, who are advised to limit their intake of high-mercury fish due to potential health risks. This means you don’t have to eliminate all fish from your pre- or post-baby diet.
20. Easily Fits Into a Balanced Diet
Tilapia is a versatile fish that can be prepared in various ways, such as grilling, baking, or sauteing, and it pairs well with a wide range of flavors and ingredients. While it is commonly found as frozen fillets, fresh options are also available.
Here are a few ways to incorporate tilapia into your meals:
- Grilled Tilapia: Marinate tilapia fillets in your favorite herbs, spices, and a bit of olive oil, then grill them until they're cooked through. Serve with a side of roasted vegetables or a fresh salad for a healthy and delicious meal.
- Baked Tilapia: Season the fillets with lemon juice, garlic, and herbs, then bake them in the oven until they're tender and flaky. Serve with a squeeze of fresh lemon juice and a sprinkle of parsley.
- Tilapia Tacos: Bread the fillets in seasoned breadcrumbs or cornmeal, then fry or bake until crispy. Serve in warm tortillas with your favorite taco toppings, such as shredded cabbage, salsa, avocado, and a squeeze of lime juice.
- Tilapia Stir-Fry: Cut tilapia fillets into bite-sized pieces and stir-fry them with colorful vegetables such as bell peppers, onions, and snap peas. Add your favorite stir-fry sauce and serve over cooked rice or noodles.









